Thinking about offering your employees a 401(k) plan? Already offer a retirement plan to your team? Either way, you’ll want all of the juicy details about the 401(k) tax credits for employers. Get the scoop on the 401(k) tax credit and how you can use it to lower your tax liability.
How tax credits work
A tax credit is a dollar-for-dollar amount businesses can use to reduce their tax liability. The credits directly lower what you owe in taxes. How much it lowers in taxes depends on the amount of the credit.
Say you have $50,000 of taxable business income. A $1,000 tax credit would directly lower your tax bill by $1,000.
Only eligible businesses or individuals can take advantage of certain tax credits. This means that you must meet specific requirements to get the tax credit.
Tax credits can incentivize business owners to add benefits to their business for employees and the work environment.
401(k) tax credits for employers
Some businesses may be eligible for a 401(k) tax credit, with a special thanks to the semi-new SECURE Act. Is yours? Keep reading below to learn about tax credit for 401(k).
SECURE Act 401(k) tax credits
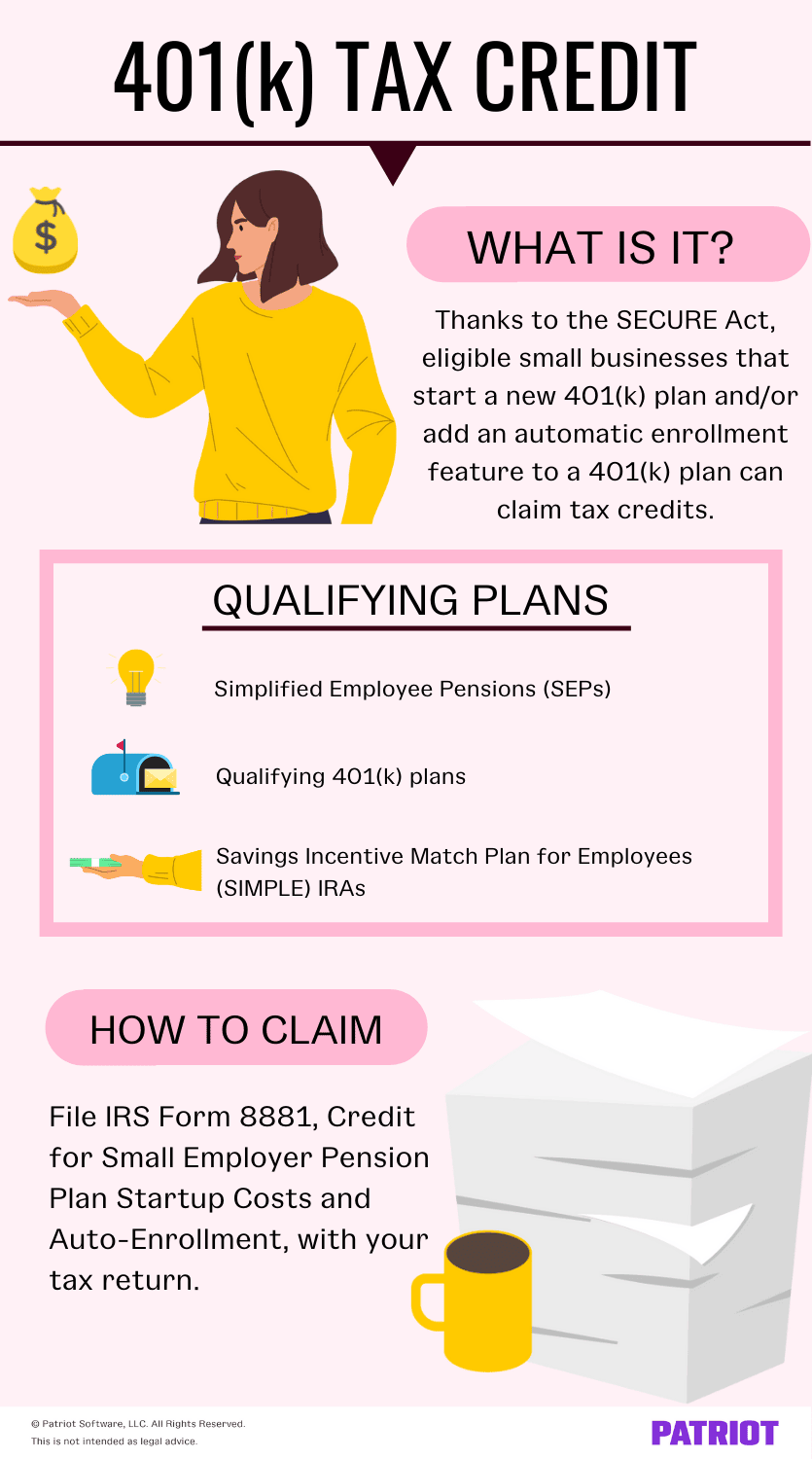
The Setting Every Community Up for Retirement Enhancement (SECURE) Act offers a number of advantages for employers who offer a retirement plan and for employees who participate.
The SECURE Act, signed into law in 2019, created enhanced tax credits for small businesses that:
- Start a new 401(k) plan AND/OR
- Add an automatic enrollment feature to any 401(k) plan
In short, eligible small businesses can receive two types of tax credits under the SECURE Act: 1. A startup costs tax credit and 2. An automatic enrollment tax credit.
The act incentivizes employers to start a 401(k) plan for their employees by offering 401(k) tax credits. And in turn, lowers a company’s tax liability.
| Looking to start a new 401(k) plan? It just got easier. Patriot has partnered with Vestwell, a retirement platform trusted by small businesses across all 50 states, to offer payroll with seamless 401(k) integration. Learn more about the upcoming integration by signing up here. |
How much is the SECURE Act’s 401(k) tax credits?
The startup SECURE Act tax credit is 50% of your eligible startup costs, up to the greater of:
- $500 OR
- The lesser of:
- $250 multiplied by the number of non-highly compensated employees who are eligible to participate in the plan OR
- $5,000
Quick side note: What are eligible startup costs? These include ordinary and necessary costs to set up and administer the retirement plan and educate your employees about the plan.
For the automatic enrollment credit, small businesses can earn an additional $500 tax credit by adding an automatic enrollment feature for employees to a new or existing 401(k) plan.
How long is the credit good for?
Eligible small businesses can claim the credits for each of the first three years of the plan. They can also choose to start claiming the credits in the tax year before the tax year when the plan becomes effective.
Both eligible startup costs and automation enrollment portions of the credit are available for up to three years.
What’s the maximum credit an employer can receive?
So, how much in total can employers receive for the 401(k) tax credits? Good question. Combined, an employer’s tax credit can get up to $5,500 per year (up to $5,000 from the eligible startup costs credit and $500 for the automatic enrollment credit).
The maximum amount per year for the credit is $5,500 and the maximum for all three years is $16,500 ($5,500 X 2).
Who qualifies for the credit?
To claim the 401(k) tax credit, you must meet all three of the following requirements:
- You had 100 or fewer employees who received at least $5,000 in compensation from you for the preceding year,
- You had at least one plan participant who was a non-highly compensated employee, AND
- In the three tax years before the first year you’re eligible for the credit, your employees weren’t substantially the same employees who received contributions or accrued benefits in another plan sponsored by your business, a member of a controlled group that includes you, or a predecessor of either
Which plans qualify for the credit?
Simplified Employee Pensions (SEPs), qualified 401(k) plans, and Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE) IRAs qualify.
A 403(b) plan and solo 401(k) plans do not qualify for the credit.
How do you claim the credit?
If you’re eligible for the credit, you can file IRS Form 8881, Credit for Small Employer Pension Plan Startup Costs and Auto-Enrollment, with your tax return.
Have questions about the form or whether you qualify? Contact the IRS directly with questions.
Where can I find more information on the retirement plan tax credit?
You can find out more information about the 401(k) startup tax credit by checking out the IRS’s website.
You can also use a 401(k) tax credit calculator to help compute how much your business’s credit may be.
Other tax credits for business owners
There are plenty of business tax credits that your company may be eligible for. So, what are they, you ask? Let’s take a quick look at some other tax credits your company may be able to take advantage of:
- Small employer health insurance tax credit
- Employers who enroll in a Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP) plan may be eligible for the small business health care tax credit if they have fewer than 25 full-time equivalent employees who pay at least 50% of employee premiums.
- Paid family and medical leave tax credit
- Employers must voluntarily offer paid FMLA leave to all eligible employees, pay at least 50% of the employee’s wages, provide at least two weeks of paid FMLA to full-time employees, and have a written policy in place.
- Disabled access credit
- An employer must have gross receipts below $1 million and 30 or fewer full-time employees.
- Work opportunity credit
- An employer might be eligible if they hire individuals from qualifying groups who have faced employment barriers (e.g., veterans, ex-felons, etc.).
- Employee retention credit
- Employers must continue to pay an employee’s wages despite not being able to operate their business due to disaster damage to qualify.
- Credit for employer-provided childcare facilities and services
- Employers who pay for certain childcare facilities and resource and referral expenses may be eligible for this credit.
Not sure about which tax credits you’re eligible for? Do some research, talk with a tax professional, or consult the IRS for more information.
This is not intended as legal advice; for more information, please click here.