The world has drastically changed in the time since the invention of computers. With the rise of the internet, working from home, and digital currency, other technologies have come into play. One of those technologies is the blockchain. What is blockchain, and how can it impact your business?
What is the blockchain?
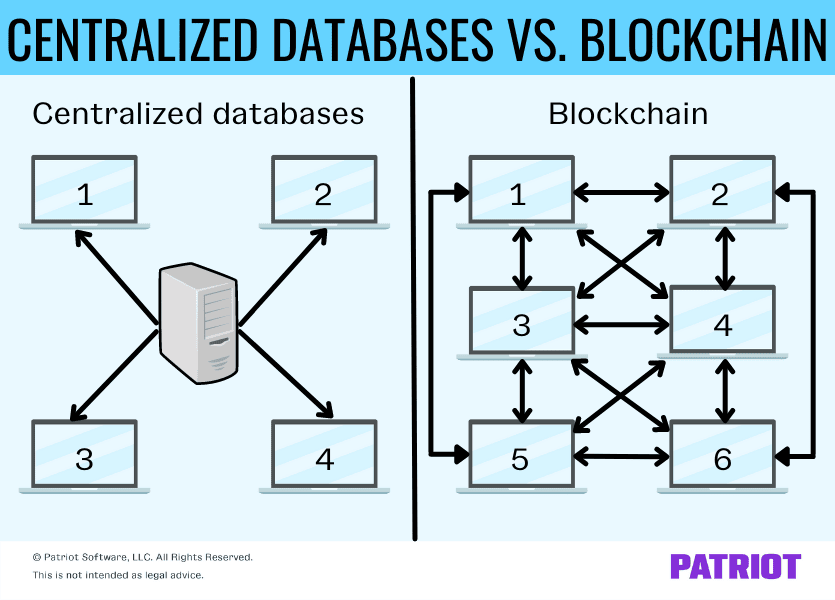
Computer databases are digital storage systems. So, what is blockchain technology? Blockchain technology is a form of computer database designed to decentralize and secure electronic data security. The new database form is unique because its design allows for security without using another trusted third party. And, the way it stores information is different from standard databases.
How does a standard computer database work? Generally, a standard database (aka a centralized database) puts data into a structured format, like a table on a spreadsheet. The database lists related information in tables and rows, and each row is called a record. The record includes data about a person, place, or thing (e.g., customers). Then, a third party typically encrypts that information.
So, how does a blockchain differ from a standard database? And, how does blockchain work? Blockchain stores data in chunks of information (i.e., blocks). Once a block is filled with data, the box locks and links to a new block where it stores more information. And, it stores each added piece of information chronologically.
Think of blockchain like a packing box. You fill the box with items, tape it closed when it’s filled, and then put a new, empty box on top to start filling. But once a box is sealed, you cannot change, alter, or destroy anything in that box.
Centralized vs. decentralized databases
Again, standard databases are centralized. What does that mean? A centralized database means that one desktop, server, or mainframe computer holds all the electronic data in a central location. So, one person or company controls the mainframe that houses the data. Businesses may have their own central server that contains all of the information for the company in one location.
By contrast, a blockchain is decentralized. The data held in the blockchain database is spread out among different networks, creating multiple copies of the information to ensure the accuracy of the information. This is why the information in a blockchain is irreversible and “locked” when the block is filled. Changing information in one copy of the blockchain does not change the information in other copies, so the information remains locked and permanent.
In a decentralized database, no one person or company controls the database. Instead, the database is spread across multiple sources to create a shared database.
How does blockchain protect data?
Blockchain tech does not rely on trusted third parties to protect the data in a database. Instead, the blockchain uses the technology’s decentralized nature to protect the data.
In a standard database, a computer virus can infect the entire server because the information is stored in one area. A computer hacker can unleash a virus, worm, or another type of malware into the computer system to corrupt or delete data. If this happens, the information is lost. Or, you could spend a lot of time trying to recover the data.
All too often, a centralized server is the only copy of the data. In that case, losing the data due to malicious software can lead to disaster.
With a blockchain, the data is spread out over multiple sources. A change in one copy does not change the other copies. And, the algorithm can quickly locate the change to one copy. So, if a hacker tries to use a virus to destroy data in one blockchain, the information is not lost. And if someone alters the information in one block of the chain, then the original data does not change with it, so the algorithm can quickly locate where the change occurred.
The process of creating copies has an added benefit. There is an established timeline and order of events in the blockchain. So, users can identify when the change took place, too.
Looking for more inside scoops on accounting and business news?
Get the latest accounting news delivered straight to your inbox.
Subscribe to Email ListOther benefits of blockchain
In addition to increased data security, blockchain provides other benefits. Blockchain technology improves accuracy for verification by relying on computers instead of human involvement. And, the tech can lower some costs because there is no need for third-party verification.
Blockchain also allows for faster financial transactions because the data is spread out. Rather than waiting for one central database to process the information, the shared blockchain allows you to process information faster.
Common uses of blockchain
Blockchain is not a new concept in the digital landscape. But, it is becoming increasingly popular due to its multiple uses. As an example, Bitcoin, a form of cryptocurrency, began using blockchain in 2009 to protect the financial transactions of users.
Now, other digital industries use blockchain, including:
- Cryptocurrencies
- Smart contracts (i.e., buyer-seller agreements written into lines of software code)
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs), also known as crypto assets
If you use cryptocurrency or accept cryptocurrency as a form of payment in your business, your data from the exchange is stored in a blockchain.
Blockchain and business
So if blockchain is typically used for activities such as cryptocurrency payments or transactions, how can you apply its use in your business? Most blockchain networks are public (e.g., Bitcoin). But, your business can create a private blockchain network run behind your corporate firewall.
You also can create a permissioned blockchain network to restrict who has access to and can participate in the network.
By using your own blockchain network, you can encrypt customer information beyond standard database storage for added security.
Keep in mind that blockchain can be an expensive system to maintain and monitor. But if your business requires the use of personal identifiable information (PII), it may be an expense to consider.
This is not intended as legal advice; for more information, please click here.